Urinary tract infections (UTIs) are common bacterial infections that affect the urinary system, which includes the kidneys, ureters, bladder, and urethra. They can occur in anyone, but are more common in women. UTIs can be uncomfortable and, if left untreated, can lead to more serious complications.
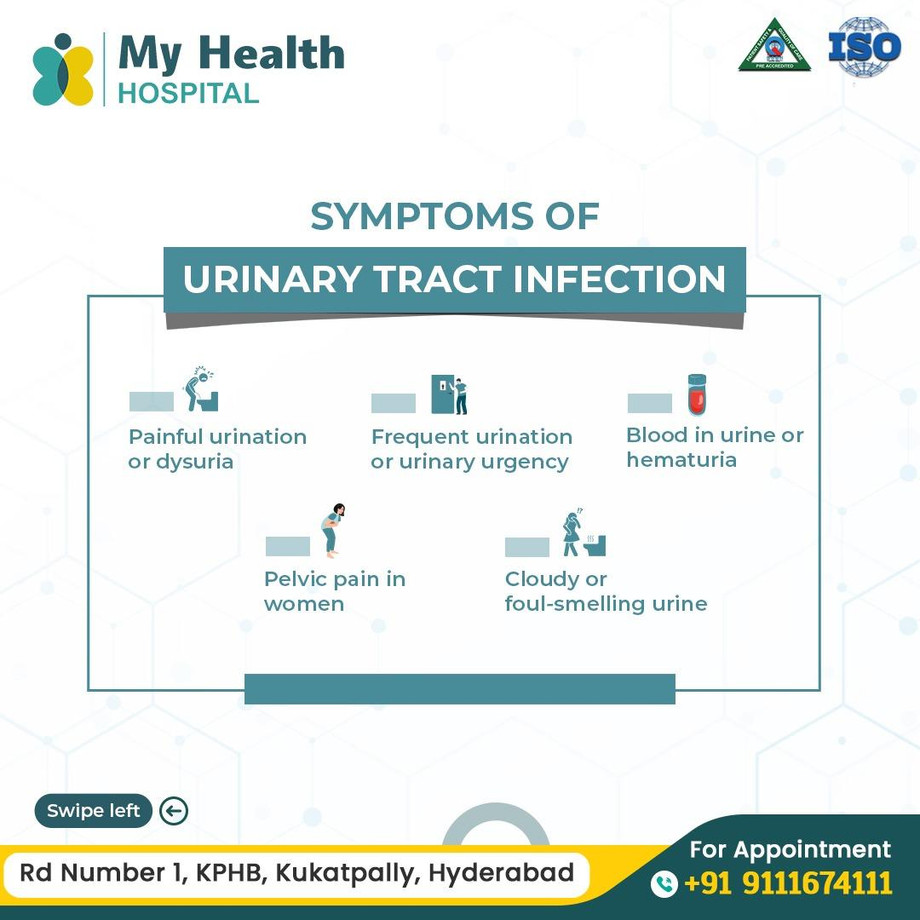
Symptoms of UTIs:
- Pain or burning sensation: During urination.
- Frequent urination: Often with only small amounts of urine.
- Urgency: Feeling the need to urinate urgently.
- Cloudy or strong-smelling urine: May indicate infection.
- Blood in urine: A sign of a more severe infection.
- Pelvic pain: In women, near the pubic bone.
Causes of UTIs:
- Bacterial invasion: Most UTIs are caused by bacteria, such as E. coli, entering the urinary tract through the urethra.
- Sexual activity: Can introduce bacteria into the urinary tract.
- Menopause: Changes in estrogen levels can make women more prone to UTIs.
- Urinary tract abnormalities: Some people are born with conditions that make them more susceptible to UTIs.
- Urinary catheters or surgery: Can increase the risk of bacterial infection.
Prevention:
- Hydration: Drink plenty of water to flush bacteria from your urinary tract.
- Personal hygiene: Wipe from front to back after using the bathroom.
- Urinate after sex: Helps flush bacteria from the urinary tract.
- Cranberry products: Some studies suggest they may help prevent UTIs.
If you experience symptoms of a UTI, it’s important to see a healthcare provider for diagnosis and treatment. Untreated UTIs can lead to serious complications, such as kidney infections.