Women's gynecological health encompasses a wide range of conditions that affect the reproductive system, from adolescence through menopause and beyond. Understanding common issues and available treatments can empower women to prioritize their health and seek timely medical care when needed. Here's an overview of some prevalent gynecological issues and their treatments:
Menstrual Disorders
1. Menstrual Irregularities:
-
- Causes: Hormonal imbalances, stress, thyroid disorders, polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS), or underlying medical conditions.
- Treatment: Hormonal contraceptives, lifestyle modifications, medications to regulate hormones, or surgical interventions in severe cases.
2. Heavy Periods (Menorrhagia):
-
- Causes: Fibroids, hormonal imbalances, adenomyosis, or bleeding disorders.
- Treatment: Hormonal therapies, nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs), endometrial ablation, or surgical options like hysterectomy in extreme cases.
Pelvic Pain
1. Pelvic Inflammatory Disease (PID):
-
- Causes: Bacterial infections typically transmitted through sexual contact.
- Treatment: Antibiotics to eliminate infection, rest, and sometimes hospitalization for severe cases.
2. Endometriosis:
-
- Causes: Endometrial tissue grows outside the uterus, causing pain and possible infertility.
- Treatment: Pain management with NSAIDs, hormonal therapies (birth control pills, GnRH agonists), or surgical options (laparoscopy) to remove endometrial tissue.
Reproductive Health
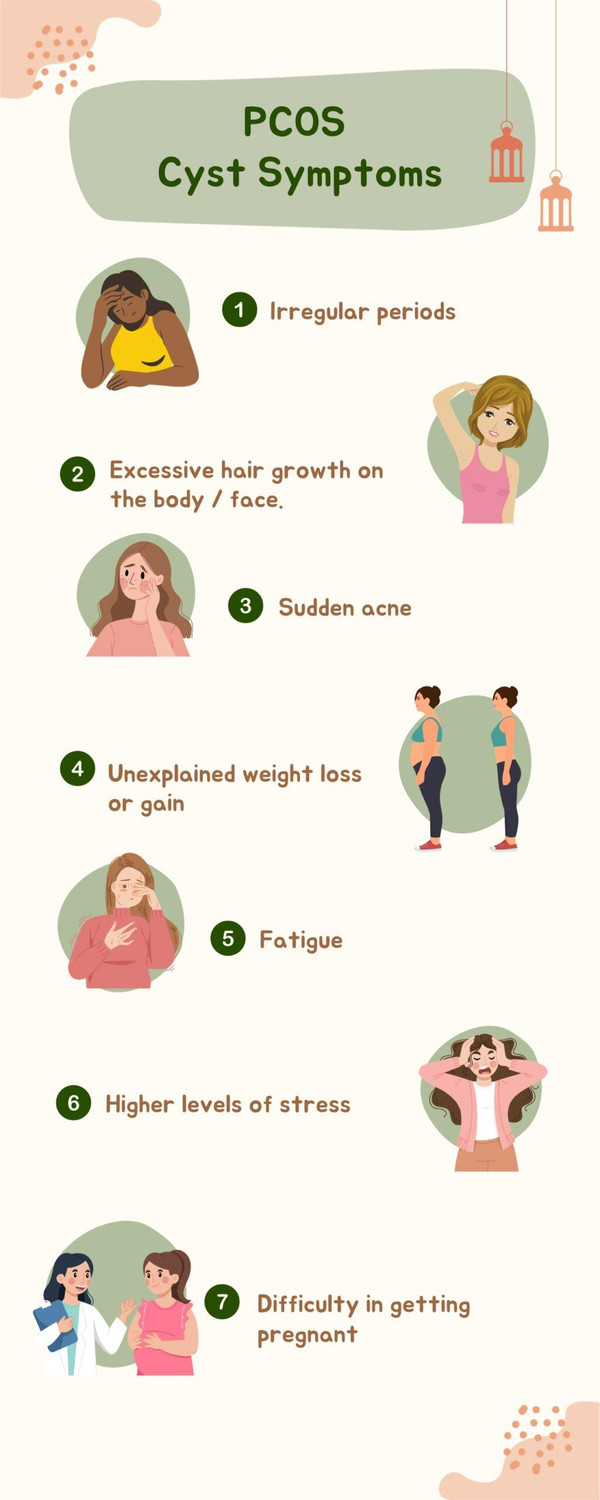
1. Polycystic Ovary Syndrome (PCOS):
-
- Causes: Hormonal imbalance leading to irregular periods, ovarian cysts, and potential fertility issues.
- Treatment: Lifestyle changes (diet, exercise), hormonal contraceptives, insulin-sensitizing medications (metformin), or fertility treatments if trying to conceive.
2. Infertility:
-
- Causes: Various factors such as ovulation disorders, blocked fallopian tubes, endometriosis, or male factor infertility.
- Treatment: Fertility medications, intrauterine insemination (IUI), in vitro fertilization (IVF), or surgical procedures depending on the underlying cause.
Menopause and Aging
1. Menopausal Symptoms:
-
- Symptoms: Hot flashes, night sweats, vaginal dryness, mood swings, and decreased bone density.
- Treatment: Hormone replacement therapy (HRT), non-hormonal medications, lifestyle adjustments, or vaginal estrogen therapy for specific symptoms.
2. Osteoporosis:
-
- Cause: Decreased estrogen levels post-menopause leading to bone loss.
- Treatment: Calcium and vitamin D supplements, weight-bearing exercise, medications to slow bone loss, and lifestyle modifications.
Sexual Health
1. Sexually Transmitted Infections (STIs):
-
- Common STIs: Chlamydia, gonorrhea, genital herpes, HPV (human papillomavirus), and HIV/AIDS.
- Treatment: Antibiotics (for bacterial infections), antiviral medications (for viral infections), and preventive measures such as safe sex practices and vaccinations (HPV).
2. Vaginal Infections:
-
- Types: Yeast infections (Candida), bacterial vaginosis (BV), or trichomoniasis.
- Treatment: Antifungal medications (for yeast infections), antibiotics (for BV or trichomoniasis), and maintaining good genital hygiene.
Routine Screening and Prevention
1. Pap Smears and HPV Testing:
-
- Purpose: Detect early signs of cervical cancer or HPV infection.
- Frequency: Recommended every 3-5 years depending on age and risk factors.
2. Breast Exams and Mammograms:
-
- Purpose: Detect breast cancer early through self-exams, clinical exams, and mammograms.
- Frequency: Self-exams monthly, clinical exams annually, and mammograms as recommended by age and risk factors.
Conclusion
Prioritizing gynecological health involves understanding common issues, recognizing symptoms, and seeking timely medical care from a qualified healthcare provider. Regular screenings, healthy lifestyle choices, and proactive management of gynecological conditions are crucial for maintaining optimal reproductive and overall health throughout every stage of life. Consult with your healthcare provider for personalized guidance and treatment options based on your individual health needs and concerns.
Credits: SAKTHI HOSPITAL & RESEARCH CENTRE