Introduction:
Today we learn about frozen shoulder. Here we discussion what is Frozen shoulder, cause, stage, pathology, symptoms or clinical feature and treatment. So let’s go.
What is Frozen Shoulder:
Frozen shoulder is a condition that is characterized by pain and restriction of the movement of the shoulder joint, especially abduction medial rotation and lateral rotation of shoulder joint.

Stage of Frozen shoulder
A. Painful or freezing stage
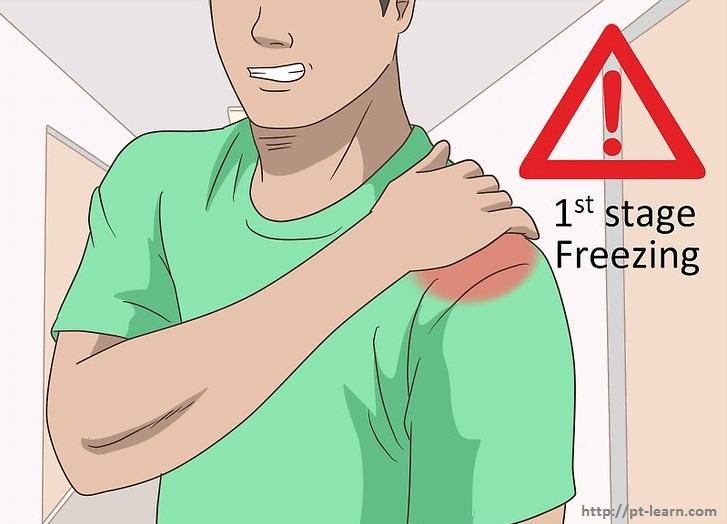
B. Frozen stage
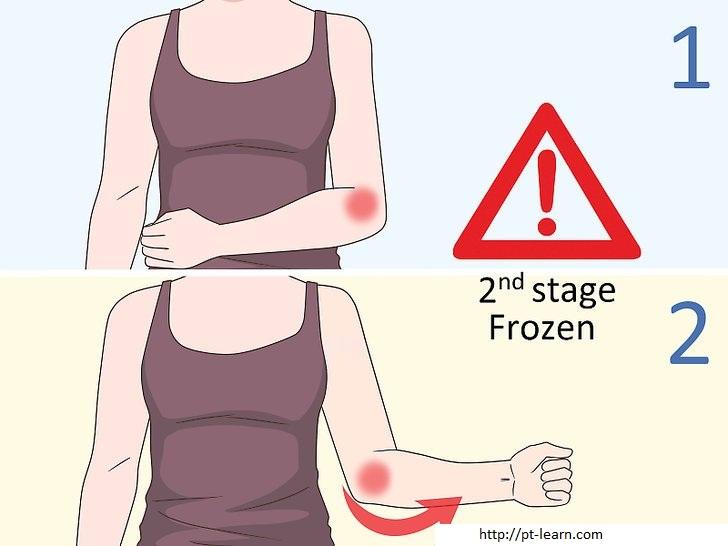
C. Thawing stage
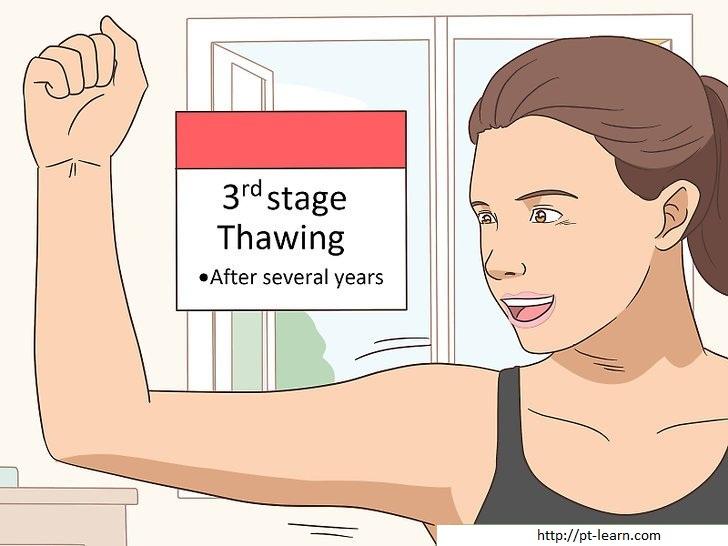
Causes of frozen shoulder:
when the capsule of shoulder joint become thicken and tighten within the joint.
- Impingement syndrome
- Supraspinatus tendinopathy
- Subacromial or subdeltoid bursitis
- Bicipital tendinopathy
- Calcific tendinitis
- Rotator cuff tear
- Early stage of adhesive cupsulitis.
Pathology of frozen shoulder:
At first when inflammation takes place on the capsule of the shoulder joint, it becomes roughness and lost its function, as a result capsule cannot provide the rhythmic free movements of the shoulder joint. Then the surrounding structures are affected due to lack or nutrition and thus also produce pain.
Clinical feature of frozen shoulder:
Frozen shoulder typically develops slowly and in three stages. Each of these stages can last a number of months.
- Painful stage: During this stage pain occurs with any movement of shoulder and shoulder’s range of motion starts to become limited.
- Frozen stage: pain may begin to diminish during this stage. However your shoulder becomes stiffer and range of motion decrease notably.
- Thawing stage: During the thawing stage, the range of motion in shoulder begins to improve.
Risk factors of frozen shoulder
Common risk factors for frozen shoulder are:
- Age: Usuallyoccurs in individual between 40-70 years of age
- Gender:This condition is found twice as often in women as in men.
- Recent trauma:Surgery or and arm fracture can lead to immobility during recovery and this may cause the shoulder capsule to stiffen.
- Diabetes:The reasons are unclear but 10 to 20 percent of people with diabetes develop frozen shoulder, and symptoms may be more severe.
Other conditions that can increase the risk are:
- Stroke
- hyperthyroidism or overactive thyroid
- hypothyroidism or under active thyroid
- cardiovascular disease
- Parkinson’s disease…Read more
