LIDAR, short for Light Detection and Ranging, is a remote sensing technique that uses laser pulses to measure distances to objects. A LIDAR scanner sends fast laser pulses to a target area and measures the time it takes for the light to return after reflecting off the objects. Here's how it works:
First, a LIDAR scanner emits laser pulses in several directions. These pulses travel at the speed of light and bounce off objects in their path.
Second, the LIDAR sensor detects the reflected laser pulses with a sensitive receiver. By measuring the time, it takes for the pulses to recover, the scanner calculates the distance to each object in its field of view.
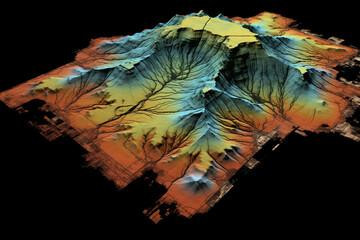
Third, as the scanner continues to send pulses and receive reflections, it creates a detailed three-dimensional map or point cloud of the area being scanned. This map contains accurate measurements of distances to objects, allowing accurate visualization of terrain, structures and other features.
In addition, advanced LIDAR systems can incorporate other sensors such as GPS and inertial measurement units to improve accuracy and geo referencing capabilities.
Finally, LIDAR scanners send out laser pulses, measure their return time and create detailed three-dimensional maps of the scanned environment. Due to its high precision and versatility, this technology finds applications in many fields such as land surveying, autonomous vehicles, forestry and urban planning.
