Introduction
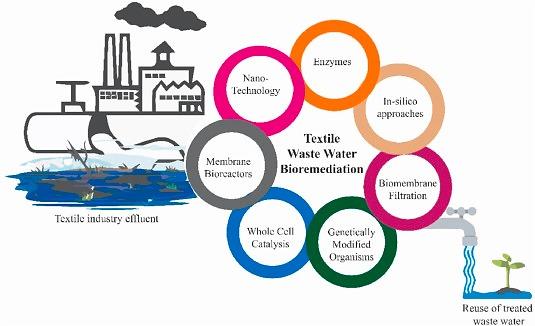
In an era marked by environmental consciousness and sustainability, the textile industry has come under increased scrutiny for its significant impact on water resources and the environment. Wastewater from textile production is often laden with dyes, chemicals, and organic matter, posing serious ecological and health hazards. In response to these concerns, various wastewater treatment methods have emerged, with bioremediation gaining prominence as an effective and eco-friendly solution. Waterman Australia, a leader in wastewater treatment solutions, has been at the forefront of utilizing bioremediation techniques to address the textile industry's environmental challenges. In this article, we delve into the principles, methods, and innovations of biological treatment in textile wastewater, focusing on Waterman Australia's expertise in this field.
An Overview of Biological Treatment
The Principle of Biological Treatment
Biological treatment, also known as bioremediation, harnesses the power of microorganisms, such as bacteria and fungi, to break down and remove contaminants from wastewater. This approach is particularly suited to textile wastewater because it effectively targets the organic dyes and chemicals that conventional treatment methods struggle to address. The key principle behind biological treatment is the metabolism of microorganisms, which transforms complex organic compounds into simpler, less harmful substances BIOREMEDIATION BIOLOGICAL TREATMENT PLANT MANUFACTURER FOR TEXTILE WASTEWATER TEXTILE EFFLUENT.
Fungal and Bacterial Removal of Dyes
One of the most significant challenges in textile wastewater treatment is the removal of dyes, which not only affect water aesthetics but also pose toxicity risks. Waterman Australia has developed specialized bioremediation systems that employ a diverse range of microorganisms, including fungi and bacteria, known for their dye-degrading capabilities. These microorganisms produce enzymes that break down dye molecules into non-toxic components. Waterman's innovative solutions ensure efficient dye removal while minimizing the need for harmful chemicals.
Microbial Fuel Cell (MFC) for Textile Effluent Treatment
Harnessing Microbial Power
Microbial Fuel Cells (MFCs) represent a groundbreaking advancement in textile effluent treatment. Waterman Australia has pioneered the integration of MFC technology into textile wastewater treatment processes. MFCs use the metabolic activity of microorganisms to generate electricity while simultaneously treating wastewater. This dual-purpose approach not only reduces energy consumption but also enhances the efficiency of pollutant removal.
Sustainable Energy Generation
Waterman's MFC-based systems are designed not only to treat wastewater but also to harness energy from the microbial activity. This sustainable energy generation aligns with Waterman's commitment to eco-friendly practices. By converting organic matter in textile effluents into electricity, the company contributes to reducing the textile industry's carbon footprint while effectively treating wastewater.
Factors Affecting Textile Effluent Degradation
pH Levels and Temperature
The effectiveness of biological treatment is highly dependent on environmental factors. pH levels and temperature play crucial roles in the activity of microorganisms. Waterman Australia's treatment systems are equipped with advanced monitoring and control mechanisms that optimize these conditions. Maintaining the ideal pH and temperature range ensures the highest degradation rates for textile effluents.
Nutrient Availability
Microorganisms require essential nutrients such as nitrogen and phosphorus to thrive and efficiently degrade contaminants. Waterman's expertise lies in balancing nutrient availability within the treatment systems. Through precise nutrient management, they ensure that microorganisms have the necessary resources for robust pollutant removal.
Toxicity and Pre-treatment
Toxic compounds in textile wastewater can inhibit microbial activity and hinder effective treatment. Waterman Australia employs pre-treatment techniques to neutralize or remove toxic substances before biological treatment begins. This strategic approach enhances the overall efficiency of the treatment process.
Conclusion
Waterman Australia's pioneering efforts in the biological treatment of textile wastewater exemplify the industry's commitment to sustainability and environmental responsibility. Through the application of bioremediation principles, fungal and bacterial dye removal, Microbial Fuel Cell technology, and meticulous attention to environmental factors, they have set a standard for effective and eco-friendly textile effluent treatment. As the textile industry continues to evolve towards more sustainable practices, Waterman's expertise in bioremediation remains a beacon of hope for cleaner water and a greener future. For textile manufacturers seeking innovative and sustainable wastewater treatment solutions, Waterman Australia stands as a testament to the power of biology in environmental stewardship.
In summary, Waterman Australia and their bioremediation methods have not only changed the way we treat textile wastewater but also serve as an inspiration for industries worldwide to embrace innovative and eco-conscious approaches to environmental challenges. Through their work, the textile industry moves closer to a future where sustainable production and responsible wastewater management go hand in hand.