Description: Design a tagging system
FR:
1. user should be able to create tag using tag name and description
2. user should be able to add tags on products
3. user should be able to search tags to add using autocomplete
4. user should be able to search products using tags
NFR:
1. highly scalable
2. low latency autocomplete
3. System should save tags efficiently i.e. to avoid duplicates and similar type of multiple tags.
4. eventual consistency . Tags created might not be immediately visible in autocomplete but will be visible eventually.(SLA - 1-2sec)
Estimations:
Tag Creation:
let's say we have 1M new tags every day
so for tag creation => 1M/10^5 => 10 tags creation/sec
Peak => 50 tags creation/sec
Tag Search:
let's say we have 1M products each day , and on each product user adds 2 tags.
so total tags added => 1M*2 => 2M
each tag is searched after 3 chars in autocomplete and estimated length of tag is 6 char
then we will have 3 req per tag search. so 2M*3 => 6M req/ day for tag autocomplete
6M/10^5 => 60 req/sec
Storage Estimation: consider each record as 10 bytes(more than enough)[ we can prove using individual column if required]
for 5 years => 1M*365*5 => 1M*1500 => 1.5GB
Apis
1. /tag
POST : Creates a tag
Payload: {tag_name, description etc..}
Verifies tag_name and creates a tag using tag_id(from verification service)
GET: get a tag
/tag/{params}
Params: {prefix, tag_id, etc..}
2. /verify_tag
POST: verifies tag and return a tag_id
Payload : {tag_name}
3. /products/tag
POST: add tag_ids to products
Payload : {product_id , tags_to_add}
Get: get tags on products
Payload : {product_id}
4. /products/search
GET: searches for products
Payload : {tag_ids:[], other filters..}
Databases:
tags[Nosql]
tag_id(primary_key)
tag_name
description
created_by
created_at
products[Nosql or sql]
product_id
tags<list<tag_ids>>
created_at
etc..
Components and Services:
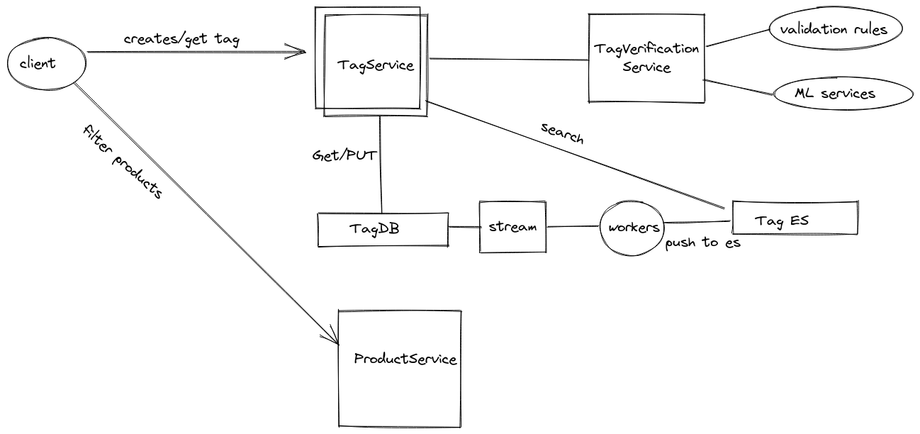
1. TagService
- exposes api's to create and search tags
- verifies tags
2. TagVerificationService
- exposes api's to provide tag_id given a tag name
3. ProductService
- exposes api's to add/update products
- exposes api's to add tags to product
- exposes api's to search products basis tag_ids and other filters
Flows:
tag_creation:
1. TagService receives a creation request with tag_name and description.
2. TagService verifies request and make a request to TagVerificationService in order to get tag_id.
3. After receiving tag_id , it saves the request into tagsDB. and returns 200 or any error to user.
4. In async, Once request is saved, either using CDC or kafka pipelines, change is pushed to a queue.
5. Worker on a queue listens and push the data in elastic search as well.
tag_search
1. TagService receives a search request , basis tag_name
2. It calls elastic search to serve the same
3. response is returned to user [{tag_id:"", tag_name"", tag_desc""}]
product_search using tag
1. user searches tags first using tag_name.
2. after receiving tags , we will make request to products_db using tag_ids
Considerations:
Verify tag creation
It is very important to verify tag creation request and generate a tag_id for the same as:
1.we can have multiple tag name with no relevant changes, like "cotton" and "Cotton" and "coTTon" all are same.we should only have one tag_id associated with it.
2.we need to remove special chars like spaces,exclamations etc. in order to make sure about data consistency.
3.we need to ensure security and keep encoding of tag_id compatible.
4.we will always display tag description of UI , but all searches will be done on tag_id only, this streamlines
our searching process.
Handling Concurrency:
creating same tags concurrently: here since we introduced tag_id as primary key, no two tags with same tag_id can exist. This is handled on DB level
Autocomplete
1. Here we can use out of box solution like elasticsearch.
2. Elastic search is a full text search engine over noSQL data,so it is directly compatible with our DB.
3. we can define index mapping type for each column , in our case tag_name will be autocomplete type mapping.
Problems:
1. Data consistency: Elastic search takes some time for indexing. Also, we are not using elastic search as our
primary DB, so data sync will have some latency, but here we can ensure eventual consistency.
2. If using elastic search is not allowed, we can use Trie for the same. We need to design separate service for trie and ensure scalability and low latency
Partition and Sharding
1. for tags_db => same indexing is used for DB and elastic search
- Shard basis tag_id: Here we can cause hotspot if one tag is used too much.
- consistent_hashing can resolve hot spot issues.
2. for product_db
- use product_id
- Additional index on "tags" column , in order to provide search using tags
Caching
1. we can cache hot tags, so that description can be fetched fast for them
2. same with product ids
3. use caching on CDN in order to further improve performance
Fault Tolerant:
1. distributed and multi-center replicated DB's
2. All of our servers are stateless deployed containers, managed by container orchestration.
we will be using a health check mechanism and in case of any non-responding container we will deploy new containers if required.
3. If cache server crashes, we can always rebuild it.(will lead to increase in few ms latency which should be acceptable)
Basic Design: