A Safe and Profitable Investment Option:
When it comes to investing money, individuals often seek safe and reliable options that offer steady returns. One such investment avenue is a Fixed Deposit (FD). A Fixed Deposit is a popular financial instrument offered by banks and financial institutions, allowing individuals to deposit a specific sum of money for a predetermined period, at a fixed interest rate. This article aims to provide an overview of Fixed Deposits, their working mechanism, interest rates offered in India, different types of FDs, factors affecting FD rates, comparisons between banks, tips to get the best interest rates, and a brief insight into DBS Fixed Deposit interest rates and promotions.
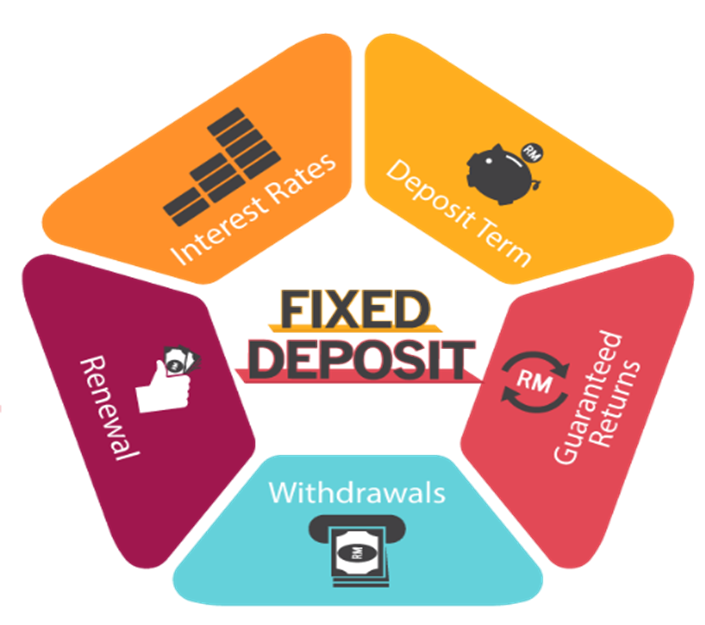
What Is a Fixed Deposit and How Does It Work?
A Fixed Deposit is essentially a financial instrument where individuals deposit a lump sum amount with a bank or financial institution for a fixed tenure, which could range from a few months to several years. The money deposited earns a predetermined interest rate, and upon maturity, the investor receives the principal amount along with the interest accrued. Fixed Deposits are known for their stability, as they offer a fixed rate of interest, which remains unaffected by market fluctuations during the investment tenure.
Rate of Interest on fixed Deposit in India:
The interest rates offered on Fixed Deposits in India vary based on several factors, including the tenure of the deposit, the amount invested, and the prevailing economic conditions. Historically, Fixed Deposit interest rates in India have been higher than those offered on savings accounts, making them an attractive investment option for risk-averse individuals. The interest rates offered can range from 4% to 7%, depending on the factors mentioned above and the policies of the respective bank.
Different Types of Fixed Deposits:
Different forms of fixed deposits are available in India through various banks. There are two types: cumulative and non-cumulative. Interest is paid on a quarterly, monthly, or half-yearly basis in cumulative deposits, whereas interest is paid on a quarterly, monthly, or half-yearly basis in non-cumulative deposits. It is determined by the investor's convenience. Let us go over the various forms of Fixed Deposits in detail.
- Standard Fixed Deposits: Standard Fixed Deposits have a fixed period and an interest rate set by the bank. The length of service might range from 7 to 10 years. Interest rates are higher than those seen in traditional savings accounts. It is the most popular FD among Stakeholders.
- Tax Saving Deposits: Tax Saving Deposits assist in tax savings and provide an exemption of up to 1.5 lakh per year. These FDs have a 5-year lock-in term during which the amount cannot be withdrawn and only one lump sum investment can be made. The amount invested is exempt under section 80C of the Income Tax Act of 1961; nevertheless, the interest earned through Tax Saver Deposits is taxable.
- Senior Citizen Fixed Deposit: Senior Citizens Fixed Deposit Scheme permits senior citizens over the age of 60 to open Fixed Deposit Accounts. These Fixed Deposit programmes offer an additional interest rate of around 0.50% above the usual Fixed Deposit Interest Rates.
- Floating Fixed Deposit: The rate on a floating fixed deposit changes quarterly or yearly, and people can benefit from shifting interest rates. The Reserve Bank of India's guidelines govern interest rate changes.
- Corporate and Other Fixed Deposits offering High ROI:
Corporate Fixed Deposits are those made by businesses for a set period of time and at a set interest rate. This form of deposit is available from financial institutions and non-banking finance companies. In this scenario, selecting a good organization is critical because it will provide higher interest rates than banks. Before investing any money, it is advisable to check these companies' credit ratings. These are unsecured because if the company fails, investors may lose their entire investment.
- NRE Fixed Deposits: NRE Fixed Deposits are for people who earn foreign cash and want to convert it to Indian rupees. The interest earned on NRE Fixed Deposits is tax-free, and the principal and interest amounts are both re-partible. However, money deposited here may be affected by currency rate swings.
- NRO Fixed Deposits: NRO Fixed Deposits differ from NRE in that the interest paid on NRO deposits is taxable at 30% under the Income Tax Act of 1961. The principal amount, as well as the interest collected, can be totally repatriated within a given bracket or specified limit. There is no risk of currency fluctuations here. The funds in the NRO Account can be invested in foreign or Indian currency.
What Factors Affect The Fixed Deposits Interest Rate?
- Investment Tenure: The investment tenure is always proportional to the interest rate. Long-term investments can always provide superior profits. In general, a 10-year FD delivers at least 1.5% to 3% better returns than shorter-term deposits. As a result, investment tenure is a critical factor in interest rates.
- Institution Type: Banks, NBFCs, and financial institutions all provide fixed deposits. Before investing, it is critical to understand the credit ratings of the institutions because, unlike banks, there is no regulatory authority to supervise the enterprises and the investor runs the danger of losing their entire investment. Fixed deposits in India are rated by credit bureaus such as CRISIL and CARE based on a variety of parameters. Any rating higher than CRISIL FAA or CARE AA is considered excellent.
- Interest Type: It is up to the investor whether they want interest paid monthly, quarterly, or semi-annually. It is known as non-compounding interest. In the case of Compounding Interest, the Fixed Deposit amount, as well as the Interest, is paid at the time of Maturity.
Why Interest Rates Differ From Banks to Banks?
- Prior to the reforms, the RBI used to set the interest rates on fixed deposits and the maturities that banks could offer. There was no competition among banks, and customers had few options as well.
- As a result of deregulation, banks are now able to set their own deposit rates for various maturities, giving investors more options.
- Previously, the RBI determined the penalty structure for pre-mature withdrawal of deposits, but this has now been delegated to banks so that banks can regulate interest rates.
- With effect from October 22, 1997, the RBI granted commercial banks the authority to set their own interest rates on domestic term deposits of various maturities with the prior consent of their respective Boards of Directors/Asset Liability Management Committees.
- Banks should pay the rates stipulated in Annex 1 and Annex 2 of the RBI circular on savings deposits and term deposits, including NRE deposits. A bank must first receive clearance from its Board of Directors/Asset Liability Management Committee before setting interest rates for various maturities.
- When a depositor asks it, the bank should allow withdrawal of a term deposit before the end of the deposit period agreed upon at the time of deposit. The bank is entitled to set its own penalty interest rate for early withdrawal of term deposits.
Conclusion: Fixed deposits are a popular investment option in India, providing a safe and secure way to grow your savings. When considering a fixed deposit, it is essential to compare interest rates offered by different banks, both public and private, and choose the one that offers competitive rates for your desired tenure. Additionally, following tips such as conducting thorough research, considering tenure, negotiating, and exploring promotional offers can help you secure the best interest rates on your fixed deposit. Always consult with the bank directly or refer to their official website for the most accurate and current information regarding fixed deposit interest rates and promotions.
