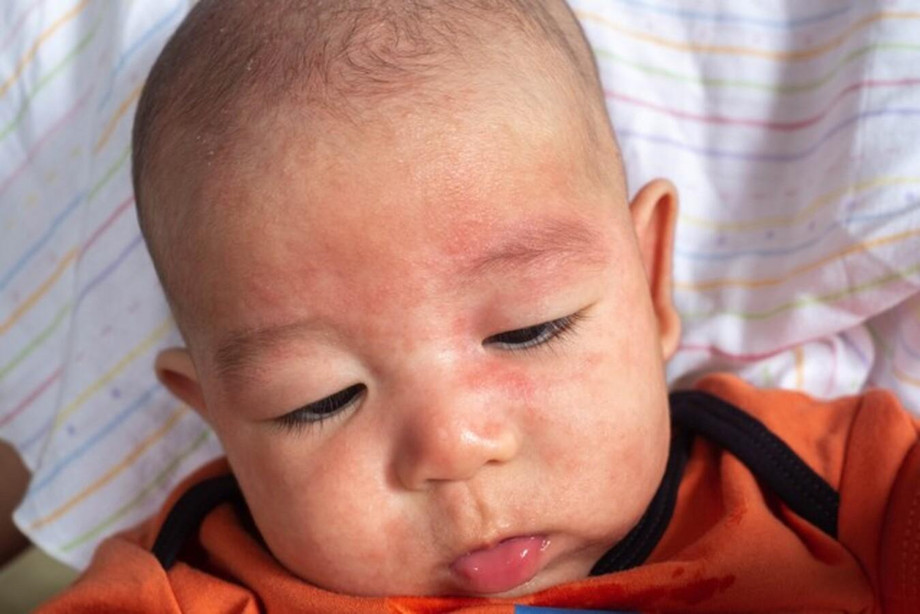
Symptoms of eczema, a common skin condition, include red, itchy, flaky and dry skin. In severe cases, skin blistering, oozing and crusting may occur. This condition is associated with a number of factors,濕疹治療 including genetics, the environment, infections, diet, medications, and emotions.
Treatment of eczema needs to be tailored to the specific condition. Treatment methods are mainly divided into two kinds: topical and oral.
1. Topical drugs:
Acute oozing lesions can use 3% boric acid solution cold compress. When the exudation is reduced, zinc oxide paste, glucocorticoid cream or gel can be used. For chronic eczema,失眠解決方法 glucocorticoid ointment or tacrolimus ointment and keratolytic agents can be used. If the lesions also have localized infections or eczema that is aggravated by bacteria or fungi, a combination of antibiotics is needed for treatment.
Glucocorticoid creams are the most commonly used topical medications for eczema. These drugs can reduce itching, redness, swelling and other symptoms, but it should be noted that long-term use will make the skin thin and fragile, affecting the barrier function of the skin, making the skin more susceptible to damage.風濕如何治療 Therefore, you need to follow your doctor's instructions when using this type of ointment, and the dosage and duration of use should not exceed the range prescribed by your doctor.
Non-glucocorticoid ointment is a new type of medication for eczema treatment. Compared with glucocorticoid, it will not cause much damage to the skin, and it has anti-inflammatory, anti-allergic, anti-bacterial and other effects, which is especially suitable for the treatment of mild eczema.
2. Oral medication:
For mild eczema, antihistamine, vitamin C and calcium can be taken orally and combined with topical medication; for severe eczema, moderate amount of glucocorticoid can be taken internally and combined with topical medication and ultraviolet light phototherapy.
Antihistamines are a common oral medication used to treat eczema. These drugs can inhibit the release and action of histamine, thus reducing eczema symptoms. Commonly used antihistamines include cetirizine and loratadine.
Immunosuppressants are medications that treat eczema by suppressing the immune system, including cyclosporine and methotrexate. These drugs are best used under the guidance of a medical professional as they have many side effects such as affecting the function of organs such as the liver and kidneys and increasing the risk of infection.
Antibiotics In the course of eczema, local or systemic infection is one of the common complications, which requires the use of antibiotics to control the infection. Commonly used antibiotics include penicillin, cephalosporins, and so on.
Overall, the treatment of eczema needs to take into account the patient's condition, the cause of the disease and other factors, according to a variety of factors for personalized treatment. One of the most commonly used is topical medication, such as glucocorticoid ointment, non-glucocorticoid ointment and so on. It is recommended to use the medication under the guidance of a professional physician or pharmacist. For the treatment of long-term, complicated eczema, doctors may choose oral medications, such as antihistamines, immunosuppressants, antibiotics and so on. During the period of medication, patients need to pay attention to timely follow-up examinations and closely observe the condition in order to promptly deal with drug side effects and adjust the treatment program.
Related Article:
5 Treatments to Make Eczema Disappear and Go Away
Eczema most afraid of repeated attacks? Do the treatment care 6 steps, no more recurrence
What are the symptoms, causes and treatment of eczema, a common skin condition?