Intrauterine insemination (IUI) is a common fertility treatment used to help couples and individuals achieve pregnancy. This comprehensive guide covers everything you need to know about IUI, including the process, success rates, potential risks, and more.
What is IUI?
Intrauterine insemination (IUI) involves placing sperm directly into a woman's uterus around the time of ovulation to enhance the chances of fertilization. This procedure is often recommended for various fertility issues and can be performed using either a partner’s sperm or donor sperm.
Who Can Benefit from IUI?
IUI is typically recommended for:
- Couples with unexplained infertility.
- Women with cervical mucus problems.
- Men with mild sperm abnormalities (low sperm count or motility).
- Couples with ejaculatory dysfunction.
- Women with mild endometriosis.
- Same-sex couples and single women using donor sperm.
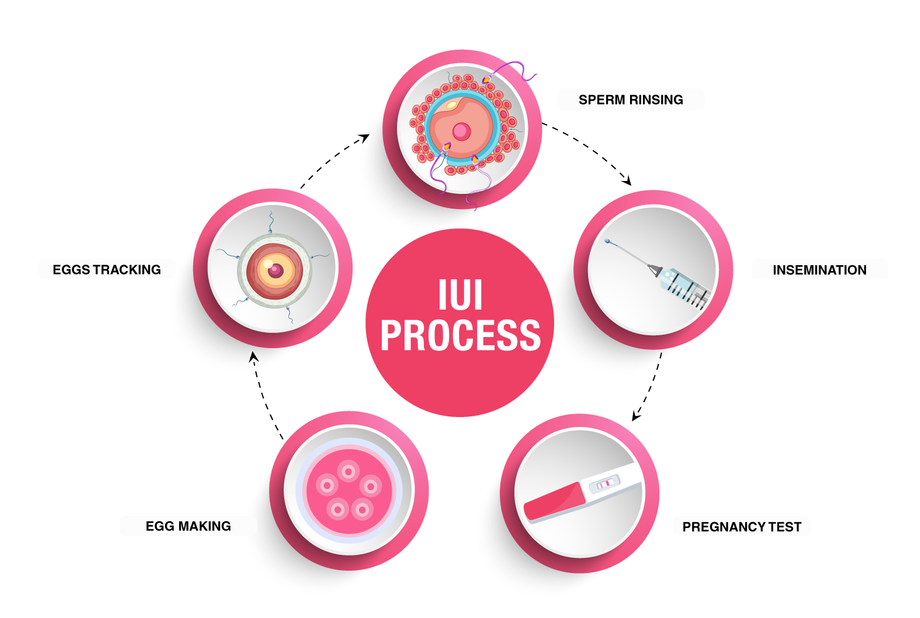
The IUI Process
- Initial Consultation and Evaluation:
- A thorough fertility evaluation is conducted, including medical history, physical exams, blood tests, and imaging studies.
- Semen analysis is performed to evaluate sperm quality and count.
- Ovarian Stimulation:
- Women may take medications (oral or injectable) to stimulate the ovaries, encouraging the development of multiple follicles.
- Monitoring through blood tests and ultrasounds helps track follicle growth and hormone levels.
- Triggering Ovulation:
- When the follicles are ready, an injection of human chorionic gonadotropin (hCG) is given to trigger ovulation.
- Ovulation typically occurs about 36 hours after the hCG injection.
- Sperm Collection and Preparation:
- On the day of the IUI procedure, a sperm sample is collected from the male partner or thawed from a donor sample.
- The sperm is washed and concentrated to remove seminal fluid and non-motile sperm, enhancing its fertilizing potential.
- Insemination Procedure:
- The prepared sperm is placed in a thin catheter.
- The woman lies on an examination table, and a speculum is inserted into the vagina to visualize the cervix.
- The catheter is gently inserted through the cervix into the uterus, where the sperm is released.
- The procedure is quick, usually taking only a few minutes.
- Post-Procedure:
- The woman may rest briefly after the procedure before resuming normal activities.
- Mild cramping or spotting is common and usually temporary.
- The Waiting Period and Pregnancy Test:
- A two-week wait follows the IUI procedure, during which the woman should monitor for pregnancy symptoms.
- A blood test or home pregnancy test is done to determine if the procedure was successful.
Success Rates of IUI
- IUI success rates vary based on several factors, including age, underlying fertility issues, and whether fertility medications were used.
- The average success rate per cycle is 10-20%, with higher success rates when combined with ovarian stimulation.
- Multiple cycles may be necessary to achieve pregnancy.
Potential Risks and Considerations
- IUI is generally safe, but there are some risks, including infection, multiple pregnancies, and ovarian hyperstimulation syndrome (OHSS).
- Discuss potential risks, benefits, and expectations with your fertility specialist.
Preparing for IUI
- Follow your fertility specialist’s instructions regarding medications and timing.
- Maintain a healthy lifestyle, including a balanced diet, regular exercise, and avoiding alcohol and smoking.
- Reduce stress through relaxation techniques such as yoga, meditation, or counseling.
Alternatives to IUI
If IUI is not successful or not recommended, other fertility treatments include:
- In vitro fertilization (IVF).
- Intracytoplasmic sperm injection (ICSI).
- Donor eggs or sperm.
- Surrogacy.
Conclusion
IUI is a valuable fertility treatment for many couples and individuals facing infertility challenges. By understanding the process, success rates, and potential risks, you can make informed decisions and work closely with your fertility specialist to optimize your chances of achieving a successful pregnancy.
Credits: EVA IVF & WOMEN'S CENTRE